 Describe what's going on in this animation.
Describe what's going on in this animation.- Work through the following two questions below.
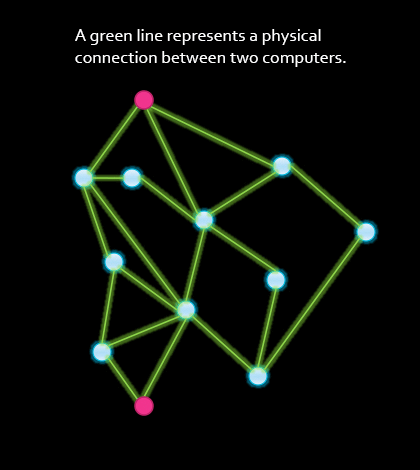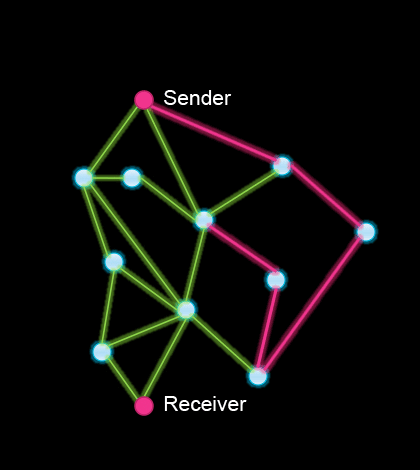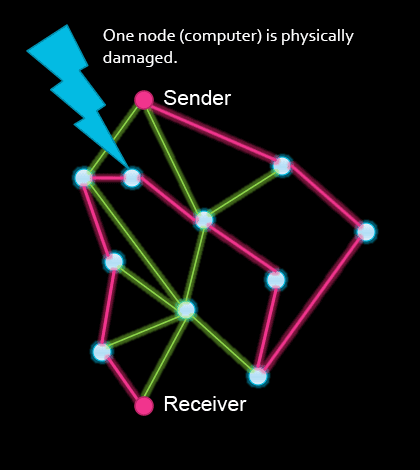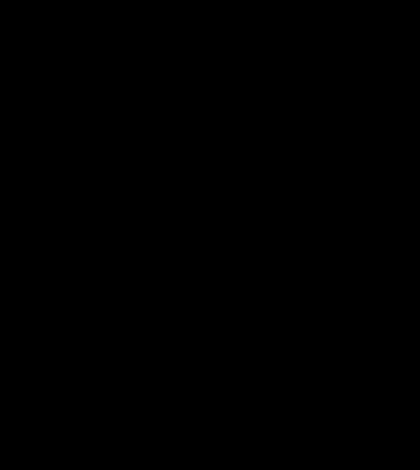
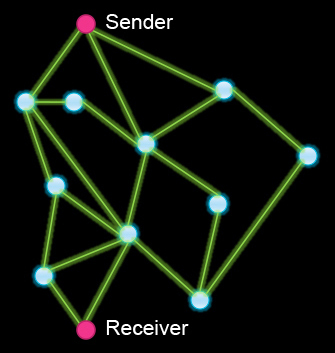 In this model of a network, what is the minimum number of nodes (connection points) that can stop working before the sender and the receiver can't communicate? (Other than the sender or the receiver themselves, of course.)
In this model of a network, what is the minimum number of nodes (connection points) that can stop working before the sender and the receiver can't communicate? (Other than the sender or the receiver themselves, of course.)
1
There are no nodes that are vital to the system. Pick any node to stop working, and you can still find another path.
2
Correct! If the node with 6 connections goes down and also either of the two to its left, the sender and receiver can't communicate.
3
Try to find a smaller number of nodes that can stop working and still break communication.
4
Try to find a smaller number of nodes that can stop working and still break communication.
5
Try to find a smaller number of nodes that can stop working and still break communication.
 In the same model network, what is the maximum number of nodes that can fail and still let Sender and Receiver communicate?
In the same model network, what is the maximum number of nodes that can fail and still let Sender and Receiver communicate?
10
If all 10 nodes fail, the sender and receiver can't communicate.
9
If 9 nodes fail, the sender and receiver can't communicate.
8
Correct! If the 4 nodes on the right and also the 4 nodes on the left all fail, the remaining 2 nodes in the middle will still allow the sender and receiver to communicate.
7
Try to find a higher number of nodes that can stop working and still ensure communication.
6
Try to find a higher number of nodes that can stop working and still ensure communication.