Making a Mathematical Library
BH and Mary need to talk about Katex style. --MF, 9/12/18
A software library is a collection of procedures that can be used in programs.
Using libraries simplifies the development of new programs. When you use procedures that you already know work correctly, you reduce the amount of time you need to spend coding, the number of possible bugs your code can have, and how much of your project you need to test.
-
Export the mathematical blocks from your U2L3-Predicates project.
-
Import these blocks into your U2L4-MathLibrary project, test them and resolve any issues, and save.
Importing Blocks
- Open the Snap! project into which you want to import blocks. (In this case, your U2L4-MathLibrary project.)
-
Import the XML file by dragging the XML file from your downloads folder into the Snap! window.
You can also import the XML file by choose "Import..." from the Snap! file menu, locating the XML file on your computer, and clicking "Open."
-
Test the blocks that you imported:
- Find the imported block(s) at the end of the palettes that contain them.
- Click each imported block to make sure it runs properly.
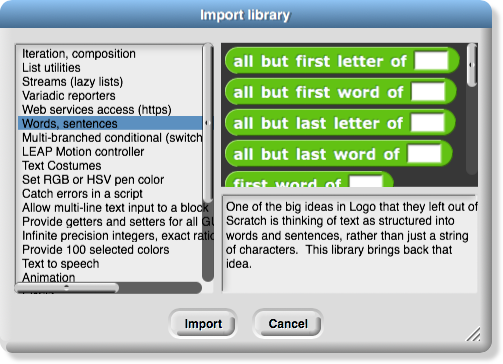
You are creating a math library. Snap
! has libraries for many things, such as one for accessing different parts of words and sentences...
Debugging Dependencies

You created your even? block using another custom block, divisible by?. If you want to use even? in another project one day, you must export both blocks in order for even? to work properly.
If you ever see this red Obsolete! block in code you have imported, it means that a required block was not exported. You'll have to go back to the original project and export again being sure to select all of the blocks needed by the blocks you want.
-
Copy and modify the code from your
even? predicate to develop an odd? predicate for your library.


You can create algorithms from scratch or by combining or modifying existing algorithms. When you are thinking of using existing code, you can either use your own code or use code from someone else's library.
-
Develop a
 block (using
block (using keep), and use it to answer these questions:
- What kinds of numbers have an odd number of divisors?
- What kinds of numbers have exactly two divisors?
You can do this on your own or follow these steps.
-
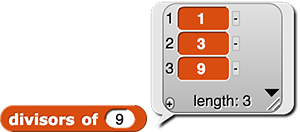
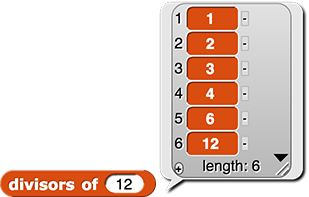
Build a
divisors block using keep.
-
Build a
number of divisors block.


-
Build an expression using
keep to answer each of these questions that were introduced above:
- What kinds of numbers have an odd number of divisors?
- What kinds of numbers have exactly two divisors?
 For each of the two questions about divisors above, determine: why do these kinds of numbers have these kinds of divisors?
For each of the two questions about divisors above, determine: why do these kinds of numbers have these kinds of divisors?
You've now made a small library, and you might want to write a list of instructions for how to use the functions in your library (for example, divisors of takes a positive integer as input and reports a list of numbers). The instructions form an Application Program Interface for the library.
:
APIs
An application program interface (API) documents what a programmer needs to know about using a library: it's a description of each procedure's purpose, inputs, and outputs (but not its algorithms).
What is a Web API?
A common kind of API is a web API in which the library exists on someone else's computer. For example, the Google Maps API describes how to embed a Google Map on your own website.
I'm actually inclined to cut all the rest of this yellow box. --MF, 1/15/20
A web API is just a call to a procedure on another machine. For example, these are three different notations for the same procedure call, which looks up the number of searches for "BJC" in the US:
The only difference is that the URL shows where on the Internet to find the procedure.
Don't cut this commented out text about PIPE until we are all set with the pipe into in U5. --MF, 8/28/19
I'm not convinced the following works here. It's a lot of text and "talking about" how pipe works. I don't believe it's going to work as a pre-teaching for 5.3 because they are likely to forget stuff, so the question is: what does it offer here? And can we do it better? For that matter, is divisors even a particularly elucidating example of using pipe? What if we offered it in the TG and combined the stuff before this todo with the MOD stuff on the previous page? Or maybe keep the two pages separate for the sake of breathing room, but move some of the quizlets and review questions at the end of that page to the end of this page (e.g. #7-9)... --MF, 8/12/19
Nested functions (that is, functions used inside of other functions, like the way you used divisible by? and numbers inside of keep) can be hard to read. Snap! offers another way to write code with multiple functions. You can use the  function from the "Frequency Distribution Analysis" library to write your code one function at at time.
function from the "Frequency Distribution Analysis" library to write your code one function at at time.

The
pipe function sends
input number through
numbers from (1) to () to report a list of numbers and then that list goes through
keep items such that ((input number) divisible by ()?) from () to get the numbers from that list that are divisible by the input number.
Notice that the empty input slots in each function are filled by the output of the previous function (or filled by the starting data in the case of the first function):
- The empty slot in the
 function is filled by input number.
function is filled by input number.
- The empty list input slot (
 ) in
) in  is filled by the output of
is filled by the output of numbers.
- As usual, the blank input slot in the predicate for
keep (that is, in  ) is filled by each item of
) is filled by each item of keep's input list (here, the output of numbers) so that keep can decide whether each number will be kept.
It's like a pipe of made of pieces connected together; the
input number goes in one end and works through each function, producing a new output at each step.
I find this description painful. If we're going to teach pipe at all, what's needed here is a
CS-Illustrated-style picture with a specific number as input and then all the intermediate values shown with arrows pointing to which empty slot each one fills. But, why do this? Is the theory that pipe will be easier for most kids than nesting? And if so, wouldn't it be easier still to make a bunch of script variables and set each one to the result of one function call? And
then show how that turns into a pipe. Or do it instead of pipe. -bh
Brian means some kind of horizontal diagram: 8 -->1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 --> 1, 2, 4, 8 --MF, 1/15/20
Pipe is a
higher order function; it is a function that takes functions as input. You've seen a higher order function before:
keep (in
Unit 2 Lab 3).
- Look at the
pipe version of divisors above.  What would happen if you did
What would happen if you did keep before numbers?
- Choose "Libraries..." in the Snap! file menu (
 ), and select and import the "Frequency Distribution Analysis" library.
), and select and import the "Frequency Distribution Analysis" library.
- Rebuild your
number of divisors block using the pipe function.
You can either create a new function called something like number of divisors 2 or pipe version of number of divisors, or you can rewrite the same block and just drag off the original report instruction but leave it inside the number of divisors block unattached from the hat block so will be saved in there but it won't run.
You don't ever have to use pipe again, but if you find it hard to write a function with a bunch of nested reporters, you can always import pipe again.
 ).
). ,
,  ,
,  , and
, and  .)
You can either deselect the blocks you don't need exported, or you can right-click the background, choose "none," and then select only the ones you want.
.)
You can either deselect the blocks you don't need exported, or you can right-click the background, choose "none," and then select only the ones you want.




 block (using
block (using 

 . (You learned about
. (You learned about  (using
(using  block may be helpful.
block may be helpful.


 function from the "Frequency Distribution Analysis" library to write your code one function at at time.
function from the "Frequency Distribution Analysis" library to write your code one function at at time.

 function is filled by input number.
function is filled by input number. ) in
) in  is filled by the output of
is filled by the output of  ) is filled by each item of
) is filled by each item of