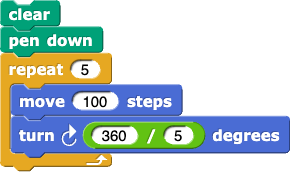
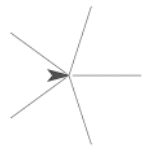
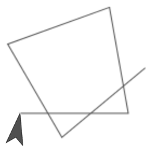
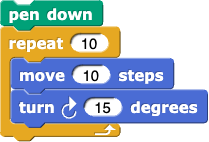
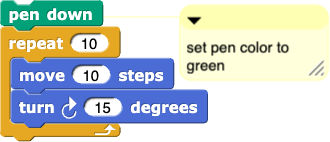
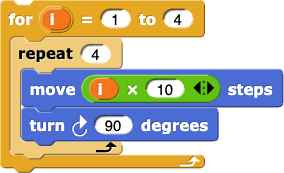
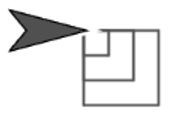
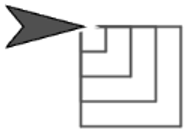
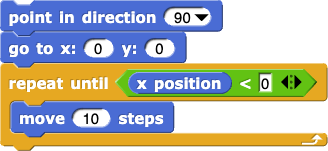
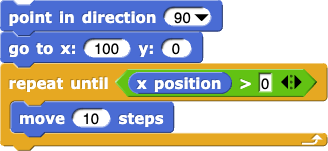
from Lab 2, Page 3
AAP-2.D
Which two of the following sentences could be reported by gossip?
For reference:
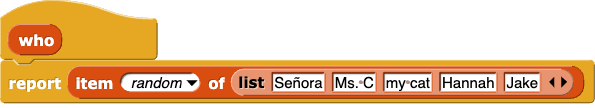



Señora and Ms. C helped.
It's true that there are two people (two "who"s) and one action (one "does what"), but they aren't in the right order. Also, the word "and" isn't anywhere in the program.
Señora ran away from my cat.
Correct! This follows the pattern: "who," "does what," "who."
Hannah listened to Hannah.
Correct! This follows the pattern: "who," "does what," "who."
Jake helped.
This sentence is missing the second "who."
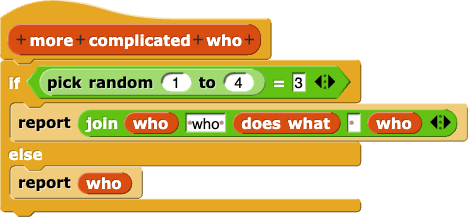 About how often will
About how often will